Learn about all things cats with this list of cat terminology.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
– A –
Ailurophobia: a fear of cats.
Ailurophilia: a love of cats.
Allogrooming: Social grooming between members of the same species, often observed in cats.
Alter: To surgically remove the ability of domestic cat to reproduce. Also known as neuter. A cat that has not been altered is unfixed.
Awn hair: Cat fur found immediately underneath the outer coat of a cat.
– B –
Barbels: The whisker-like sensory organs located around the mouth of a cat. They are used to detect changes in its surroundings.
Bicolor: A cat coat that features two distinct colors. Typically, these are white and another color.
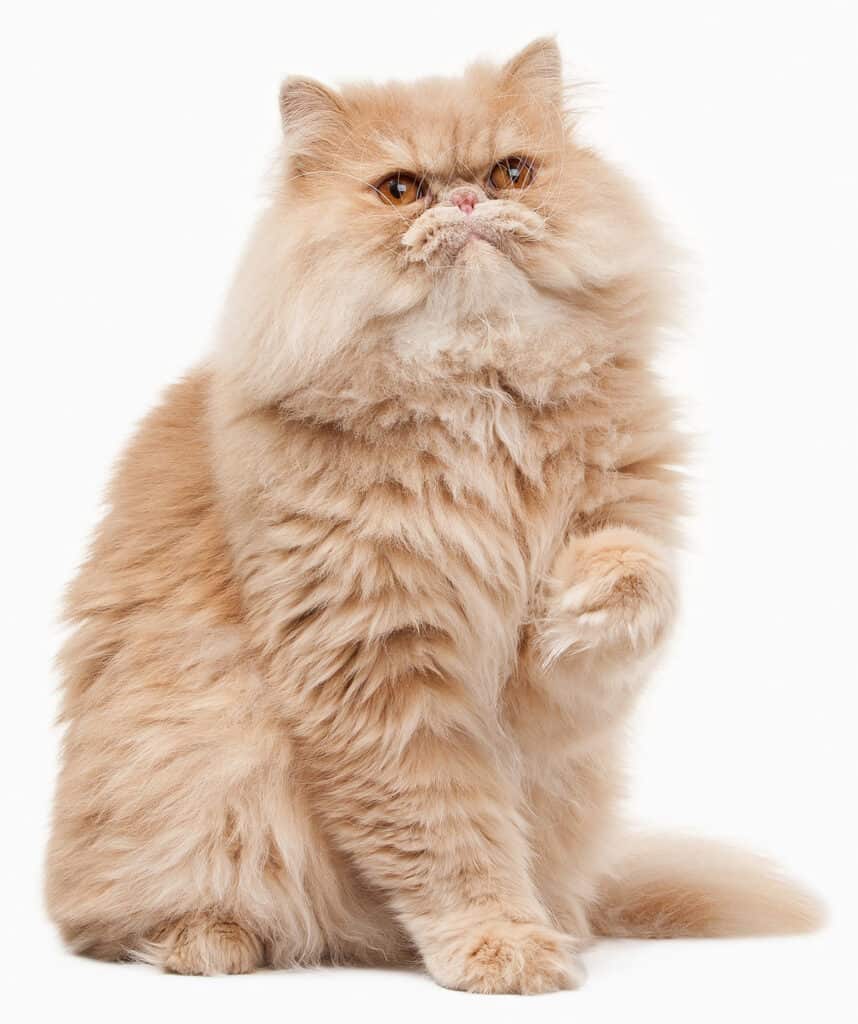

Brachycephalic: Describes cats with a short, wide skull, like the modern Persian or Exotic Shorthair.
Breed: A specific group of domestic cats that has a homogeneous appearance, recognized by cat registries. More: How Many Cat Breeds are There?
Bunting: A behavior where a cat rubs its head against people or objects, marking them with scent glands located on the cat’s head.
– C –
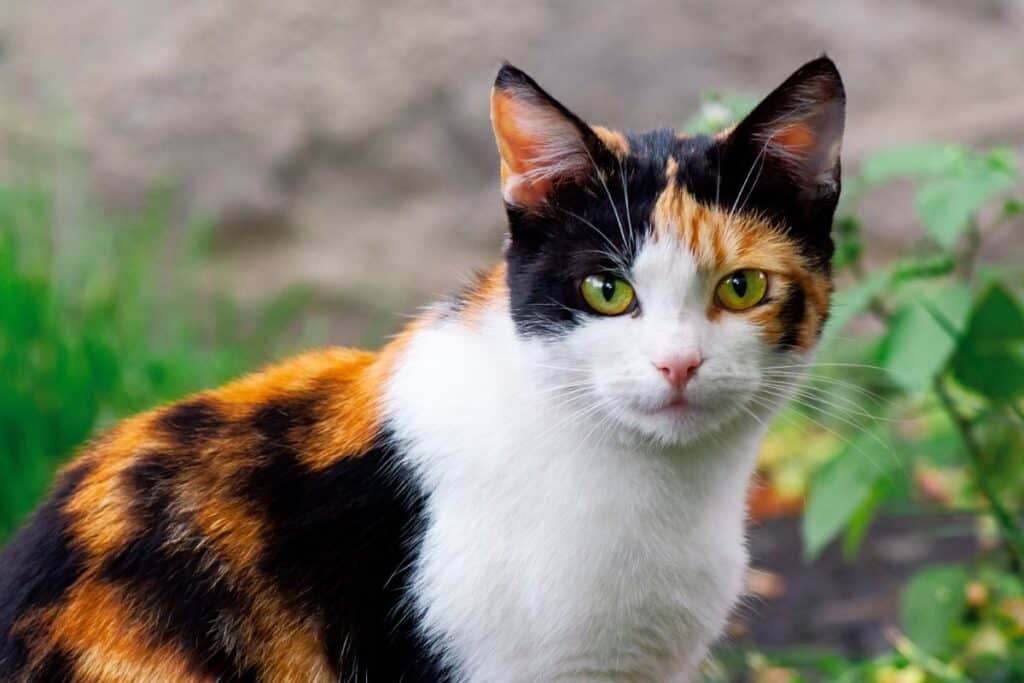
Calico: a tri-color coat pattern.

Catnip: A short-lived perennial herb (Nepeta cataria) that about two-thirds of cats will react pleasantly towards. More: Why Do Some Cats Love Catnip?
Carnivore: Animals that eat meat as their source of nutrition.
Carpal whiskers: whiskers found on the back of the forelegs of cats.
Castrate: To remove the testicles of a male cat in order to prevent the cat from being able to impregnate unfixed female cats.
Caterwaul: The shrill and loud crying of cat as a response to being unhappy. Unaltered female cats will also caterwaul when they are in heat to alert males in the area.
Cat Tree: A piece of cat furniture with multiple levels, platforms and often a scratching post.
Chattering: A sound that cats make when they see a bird or a squirrel, usually from a window.
Clowder: A group of three or more cats.
Colony: A group of stray and/or feral cats that coexist around a food source for protection. Colonies tend to be mostly made up of female cats.
Community cat: A stray or feral cat that lives outside and is provided with food and shelter by a human caretaker. These cats are also sometimes called garden cats.
– D –
Desex: To neuter or alter a cat.
Desensitization: Gradual exposure to a stimulus that a cat finds fearful or stressful to reduce their reaction to it.
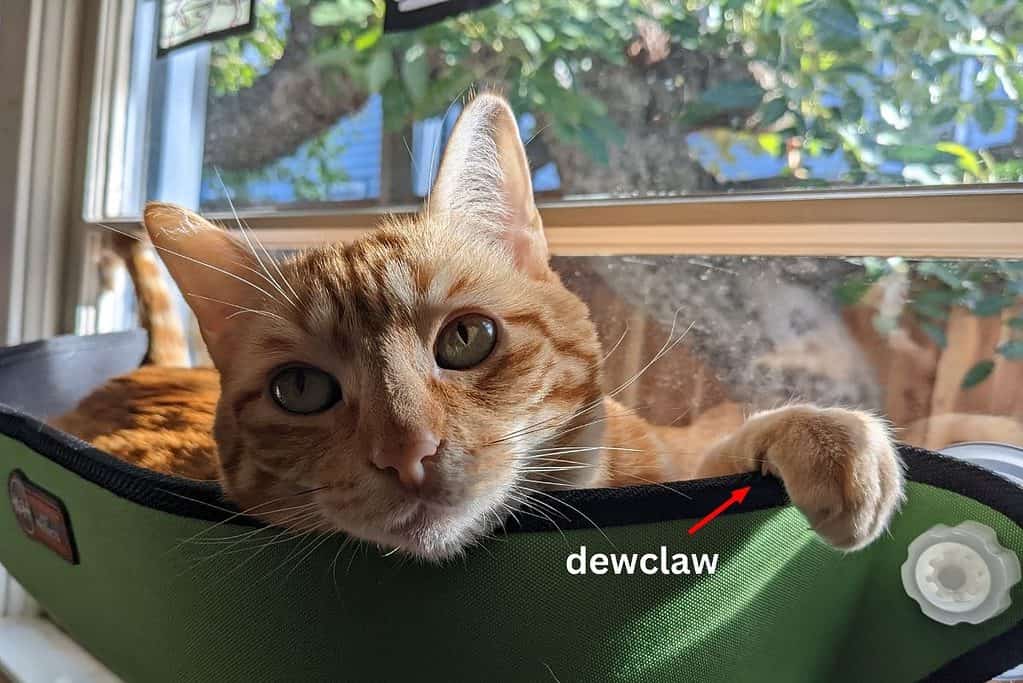
Dewclaw: The fifth claw on the front paws. Somewhat similar to a thumb on a person, the dewclaw is in an elevated position from the bottom four claws on the front paws of a cat. The declaw grows on the inside of the front paws.

Digitigrade: Animals that walk on their toes. Cats are digitigrade animals.
Dilute: A color term used to describe lighter or “washed out” colors, like blue (dilute black) or cream (dilute red).
Domestic cat: A house cat. The domestic cat is the only domesticated species in the family Felidae.
Domestic Shorthair (DSH): A term used to describe a cat of mixed ancestry with short fur. More: Facts About the Domestic Shorthair Cat
Domestic Longhair (DLH): Similar to a DSH but with long fur.
Down fur: the third and innermost layer of cat fur. Down fur serves as a insulating layer to keep the cat warm.
– E –
Ear tipping: A universally recognized sign that a feral cat has been neutered or spayed. It involves removing approximately a quarter of the tip of the cat’s left ear in a straight line cut.

Enrichment: Activities, toys, and other items that stimulate a cat’s mind and help to satisfy their natural instincts.
Estrus: The fertile part of a female cat’s reproductive cycle. Also known as being “in heat”.
– F –
Feline: A cat or something relating to or affecting cats.
Feral cat: A domestic cat that has never been handled or acclimatized towards humans. Feral cats have never lived inside a house and are wild. Feral cats avoid human contact.
Flehmen response: That weird face cats making when examining an unusual and intriguing smell. Also known as gaping in cat, felines will often look like they have smelled something bad but they are really just taking an extra deep smell to figure out what the scent is.

Free-roaming: Domestic cats that are not confined to a house. Also known as outdoor or indoor/outdoor cats.
Frenetic random activity periods or FRAPs: the technical term for the cat zoomies. FRAPs are intense and short-lived bursts of pent up energy by cats that typically happen during the evening.
– G –
Gaping: Similar to the Flehmen response seen in other large mammals, cats will draw scents deeper in a scent organ located on the roof of their mouth. While the cat may look like they are reacting negatively to a smell, this behavior allows the cat to essentially smell deeper and be able to distinguish between similar smelling scents.
Gib: a neutered male cat.
Guard hairs: Guard hairs are long, coarse hairs that form the outer coat of the cat. These are the hairs that stand up when a cat is scared.

– H –
Hairball: A hairball is an elongated clump of hair formed when swallowed fur gathers undigested in the cat’s stomach. Cats will vomit this clump of fur back up.
Hiss: The snake-like sound that a can makes when a force of air is passed over the curled tongue. Cats typically hiss when scared or angry.

Hypercarnivores: Cats and minks are the only two domestic animals considered hypercarnivores. Hypercarnivores are animals that required at least 70% of their diet as meat.
– I –
In Heat: The fertile period of a female cat’s reproductive cycle. Females cats who have been spayed do not go into heat. Also known as estrus.
Intact: A cat that has not been altered.
– J –
Jowls: Thickening of the skin of the cheeks of unaltered male cats that form as the result of testosterone.

– K –
Kindle: A group of kittens.
Kitten: a juvenile cat, typically under the age of six months.

Knead: Kneading is an action by cats in which they relax and push out and pull in their front paws, frequently alternating between the right and left limbs. More: Why Do Cats Knead?
– L –
Litter: a group of kittens born at the same time from the same mother.
– M –
Marking: When a cat deposits its scent (through urine spraying or rubbing) onto objects, places or people to mark its territory.
Microchip: A tiny device implanted under a cat’s skin that stores identification (such as the cat owner’s phone number and address) information retrievable by a scanner.
Moggy (or moggie): a non-pedigree cat of mixed or unknown ancestry. These cats are sometimes referred to as domestic shorthaired or domestic longhaired cats depending on the coat length.
Molly: a neutered female cat.
– N –
Neuter: To remove the ability of a cat to reproduce by surgical means. Also know as to alter. A cat that has not been neutered is unfixed.
Nictitating membrane: A transparent inner eyelid that can be draw across the eye to protect the cat from debris and dust.
– O –
Obligate carnivore: Cats are obligate carnivores and therefore depend only on meat for survival.
Overgrooming: When a cat grooms itself excessively, potentially leading to hair loss and skin irritation.
– P –
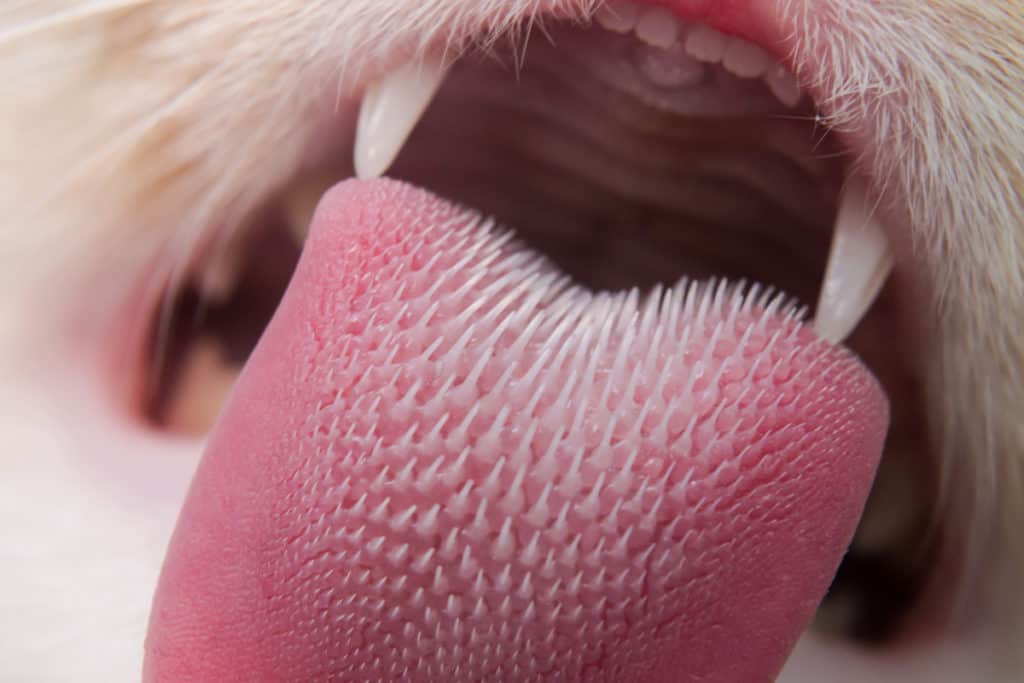
Papillae: spines that cover a cat’s tongue. Papillae serves as barbs that help to pull liquid into the cats mouth and remove dirt and hair when grooming.

Petting aggression: Petting aggressiveness is a reflexive response of biting or clawing by cats who dislike being pet. More: Why Do Some Cats Bite When You Pet Them?
Pheromones: chemicals that a cat secretes that triggers a social response in other cats. More: What are Cat Pheromones, and Do They Work to Calm Cats?
Pica: A compulsive behavior where a cat eats non-food items like fabric or plastic.
Piloerection: the upright raising of hair along the back as a response to fear by a cat.

Polydactyl: To have more than five toes on one or more paws. More: Facts About Polydactyl Cats
Primordial pouch: Loose fur on the belly that provides jumping flexibility and protects the cat’s organs during fights. More: Why Do Some Cats Have Loose Skin?

Purr: A vibrating sound cats produce in their throats that can indicate happiness, a demand for food, or fear. More: How Cats Communicate Through Purring
– Q –
Queen: An unspayed female cat.
Queening: The process of a female cat getting ready to give birth. Also known as ‘kittening’.
– R –
Retractable claws: Domestic cats have claws that are sheathed and can retract and therefore partially hide inside the paw. This retraction protects the claw from wear and tear and allows the cat to walk silently when pursuing prey.
Righting reflex: Cats have a flexible spine and can rotate their hind legs, which allows them to land on their feet from falls from great heights. This is known as the “righting reflex”.
– S –
Shedding: The process of a cat losing individual hairs. Cats will shed on a daily basis but shedding will become more frequent and intense as the cat grows out their winter fur.
Socialization: The process of exposing a cat to humans, other animals, and various environments to help the cat feel comfortable and confident.
Spay: To alter or neuter a female cat.
Spraying: A form of scent marking where a cat sprays a small amount of urine on a vertical surface, often performed by unneutered males.
Stray: A formerly owned domestic cat that is now living in the wild. Strays can be friendly towards humans or avoid human contact. More: Facts About Feral and Stray Cats

Stropping: The act of a cat sharpening their claws.
Superfecundation: Kittens in the same litter can have different fathers. This is known as superfecundation.
– T –
Tabby: Distinctive types of coat patterns on some cats that evolved for camouflage. More: What are Tabby Cats?

Territory: An area that a cat claims as its own and defends against other cats.
Tomcat: An unfixed male cat. Also known as a tom. Tomcats, unlike male cats which were neutered before the onset of puberty, have jowls. Tomcat jowls are fleshy regions that form in the cheeks of unaltered male cats as a result of testosterone’s effects.
Tortoiseshell: Cats with a patchwork combination of two colors other than white. Also known as torties.
Trap-Neuter-Return (TNR): The process of trapping feral cats, neutering them, and then returning them back to where they were caught.

Tuxedo: A cat with black and white fur that appears as if it’s wearing a tuxedo.
– U –
Undercoat: The layer of fur closest to a cat’s skin. It helps keep them warm and provides a degree of waterproofing. Some breeds have a more pronounced undercoat than others.
Unneutered: Refers to a cat, typically a male, that has not been neutered or castrated, and is therefore capable of reproducing.
Urine Marking: A behavior in which cats mark their territory by spraying urine, often in response to stress or changes in their environment.
– V –
Vacuum effect: The repopulation of an area by other feral cats after the capture and removal of the existing cat population. The incoming cats move in to take advantage of the existing food source.
Vellus hair: The fine, downy hair found on hairless cats.
Vibrissae: Stiff, functional hair also known as whiskers. Vibrissae are used by cats to sense their environments.
– W –
Whisker fatigue: Overstimulation of whiskers which can cause pain in cats. Whisker fatigue is commonly caused when the whiskers of a cat brush against the sides of too small feed and water bowls.
Whiskers: Stiff, functional hair used to sense a cat’s environment. Also known as Vibrissae. More: Where Do Cats Have Whiskers?

– X –
X-Chromosome: Cats have two sex chromosomes, X and Y. A female cat has two X chromosomes, and a male cat has one X and one Y chromosome. The X chromosome carries the gene that determines the color of the cat. This is why male cats can only be orange or black unless there is a genetic mutation, but female cats can be tortoiseshell or calico.

– Y –
Yellow Fat Disease: Also known as steatitis, Yellow fat disease a rare condition in cats where there’s inflammation of the body’s fat. It can occur when a cat’s diet is too rich in unsaturated fatty acids and deficient in vitamin E.
Yowl: A type of vocalization produced by cats, often long, drawn-out, and mournful sounding. Cats may yowl for various reasons, including distress, discomfort, mating calls, or due to medical conditions.
– Z –
Zoomies: An informal term used by pet owners to describe sudden bursts of energy causing pets, including cats, to run or jump around seemingly without reason. The scientific term for the zoomies is Frenetic random activity periods or FRAPs. Zoomies typically happen with cats in the early evenings.
This article was first published on February 6, 2021 and has since been updated.